Urticaria
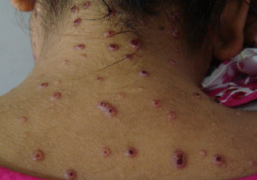
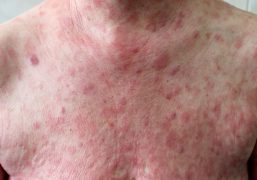
Urticaria, also known as hives, is a skin condition that causes itchy, raised, red or white welts (also called wheals) on the skin. These welts can be small or large, and may appear in clusters or spread across a large area of the body. They can appear suddenly and disappear just as quickly, often within a few hours, but in some cases can last for days or even weeks.
The most common cause of urticaria is an allergic reaction, such as to certain foods, medications, insect bites, or environmental allergens such as pollen or pet dander. However, it can also be caused by non-allergic triggers such as stress, heat, pressure on the skin, or infections.
In most cases, urticaria is not a serious condition and can be treated with over-the-counter antihistamines, which can help reduce itching and swelling. If the urticaria is severe or recurrent, prescription medications such as corticosteroids, immunosuppressants or biologic agents may be needed. Avoiding triggers is also an important part of managing urticaria.
It’s important to seek medical attention if urticaria is accompanied by other symptoms, such as difficulty breathing, swelling of the face or throat, or if it persists for more than a few days, as it may be a sign of a more serious condition.