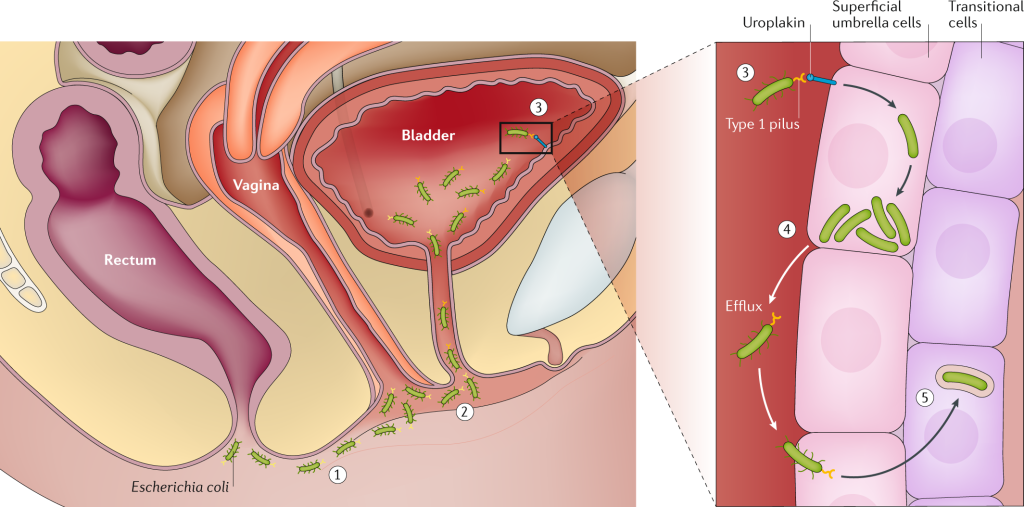
Urogenital infection
Urogenital infections are infections that affect the urinary and reproductive organs, including the bladder, urethra, kidneys, prostate gland, and genitals. These infections can be caused by bacteria, viruses, fungi, or parasites and can affect people of all ages and genders.
Common symptoms of urogenital infections may include painful or frequent urination, lower abdominal or pelvic pain, blood in the urine, cloudy or foul-smelling urine, discharge from the genitals, and pain during sexual intercourse.
Treatment for urogenital infections depends on the underlying cause and severity of the infection. In many cases, antibiotics or antifungal medications may be prescribed to help clear the infection. Pain relievers and anti-inflammatory medications may also be recommended to help manage symptoms such as pain and swelling.
In addition to medical treatment, there are several steps you can take to help prevent urogenital infections. These include practicing good hygiene, avoiding sexual activity with infected partners or using condoms, drinking plenty of fluids to help flush out bacteria, and urinating after sexual intercourse to help flush out any bacteria that may have entered the urinary tract.
If you suspect you may have a urogenital infection, it is important to seek medical attention as soon as possible. Your healthcare provider can help diagnose the infection and develop an appropriate treatment plan to help manage symptoms and prevent complications.