Urinary Tract Infection
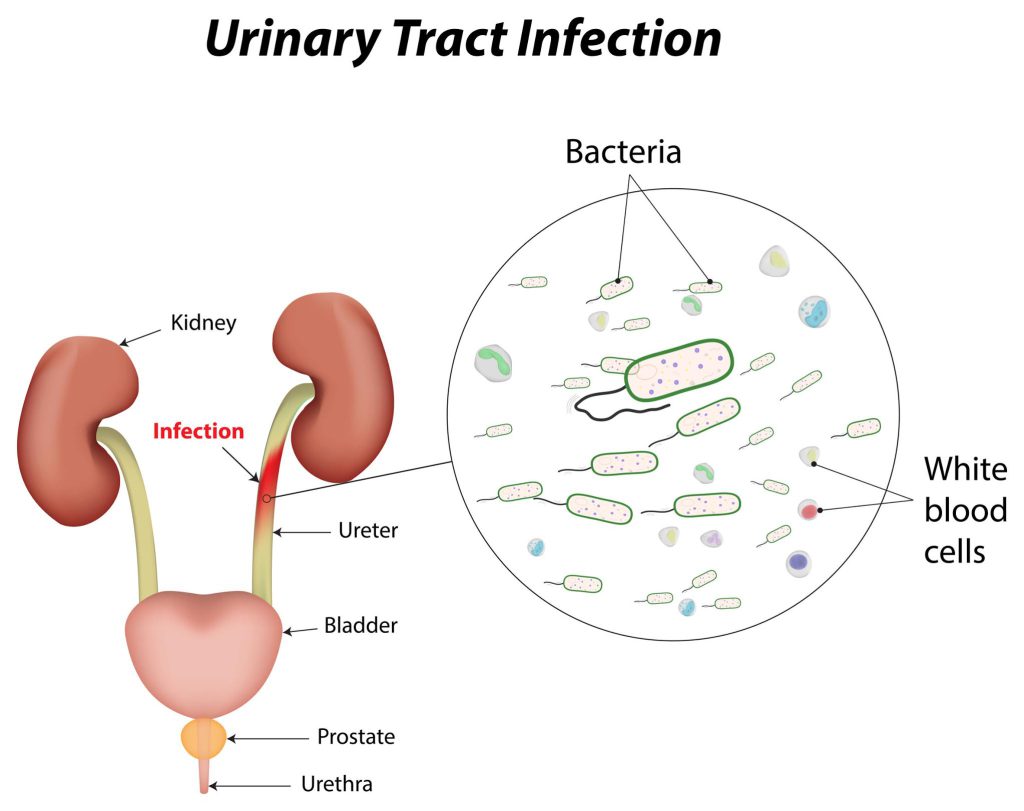
A urinary tract infection (UTI) is an infection that affects any part of the urinary system, which includes the kidneys, bladder, ureters, and urethra. UTIs are typically caused by bacteria, but can also be caused by fungi or viruses. They are more common in women than men.
The symptoms of a UTI can include pain or burning during urination, frequent urination, a strong urge to urinate, cloudy or strong-smelling urine, and pain or pressure in the lower abdomen or back. In severe cases, fever and chills may also occur.
UTIs are typically diagnosed through a urine culture, which can identify the type of bacteria causing the infection and guide treatment.
Treatment for a UTI usually involves a course of antibiotics, which can help to eliminate the bacteria causing the infection. Pain relief medications may also be recommended to manage symptoms.
Prevention of UTIs includes good hygiene practices, such as wiping from front to back after using the bathroom, drinking plenty of water, and urinating frequently to help flush bacteria out of the urinary system. In some cases, antibiotics may be prescribed prophylactically to help prevent recurrent UTIs in individuals who are prone to them.
If left untreated, UTIs can lead to more serious complications such as kidney damage or a bloodstream infection, so it is important to seek medical attention if you suspect you may have a UTI.