Sporotrichosis
Sporotrichosis is a type of fungal infection caused by the fungus Sporothrix schenckii. The fungus is commonly found in soil, plants, and decaying vegetation, and can infect humans and animals.
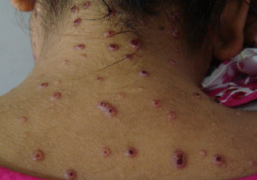
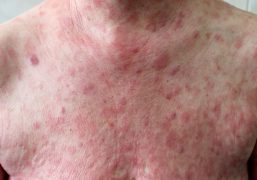
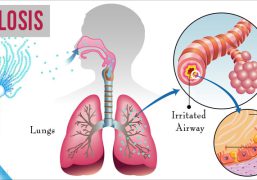
Sporotrichosis usually affects the skin, causing small, painless bumps or ulcers that can appear days or weeks after exposure to the fungus. The bumps may develop into larger lesions and can spread along the lymphatic system, causing swollen lymph nodes. In some cases, the infection can spread to other parts of the body, such as the lungs or bones, although this is rare.
Diagnosis of sporotrichosis is typically done by a skin biopsy or culture of the affected area. Treatment typically involves antifungal medications, such as itraconazole or terbinafine, which can be administered orally for several weeks or months depending on the severity of the infection. In severe cases, intravenous antifungal medications may be required.
Prevention of sporotrichosis involves avoiding exposure to the fungus by wearing protective clothing, gloves, and masks when handling plants or soil. Individuals who work in industries or hobbies that involve exposure to soil or plants, such as horticulture, farming, or landscaping, should take extra precautions to avoid exposure to the fungus.