Skin and Soft Tissue Infection
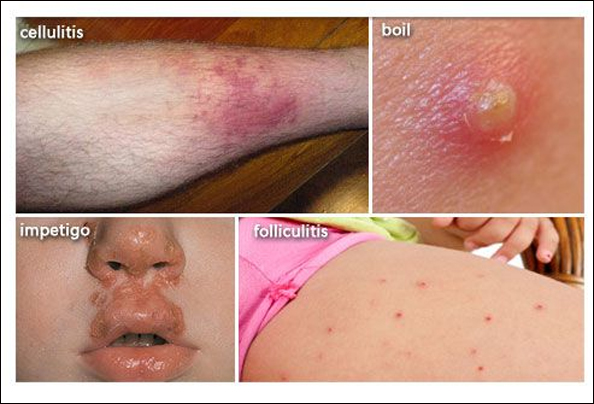
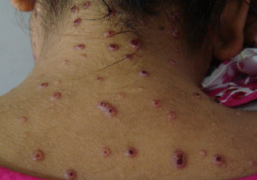
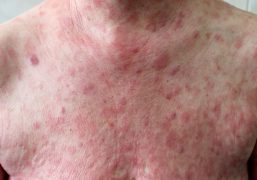
Skin and soft tissue infections (SSTIs) are infections that involve the skin, underlying tissue, and/or subcutaneous fat. They can be caused by a variety of bacteria, including Staphylococcus aureus and Streptococcus pyogenes. SSTIs can range from mild infections such as impetigo or cellulitis to more severe infections such as necrotizing fasciitis.
The symptoms of SSTIs can include redness, warmth, swelling, pain, and/or drainage from the affected area. Some SSTIs can also cause fever and chills. Diagnosis of SSTIs is typically made through physical examination and laboratory tests, such as cultures of any discharge or tissue samples.
Treatment for SSTIs typically involves a course of antibiotics, which can help to eliminate the bacteria causing the infection. In some cases, incision and drainage of the affected area may also be necessary to help remove any pus or debris.
Prevention of SSTIs includes good hygiene practices, such as washing hands regularly and keeping cuts and wounds clean and covered. It is also important to avoid sharing personal items such as towels or razors, and to avoid contact with individuals who have active SSTIs.
If left untreated, SSTIs can lead to more serious complications such as sepsis or tissue damage, so it is important to seek medical attention if you suspect you may have an SSTI.