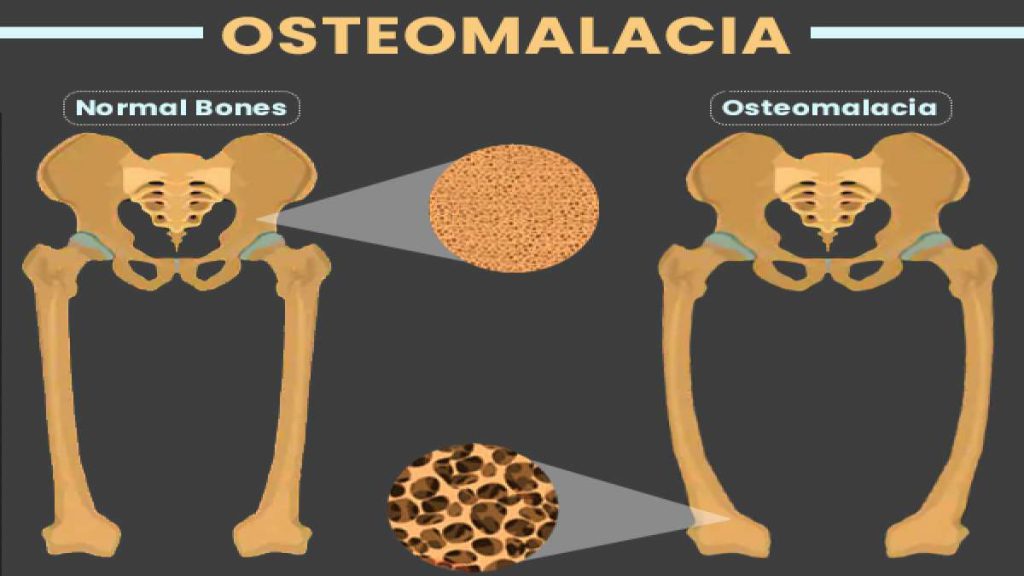
Osteomalacia
Osteomalacia is a condition in which bones become soft and weak due to a deficiency of vitamin D, calcium, or phosphate. Here are some ways to manage osteomalacia:
- Vitamin D and calcium supplements: Treatment typically involves high-dose vitamin D and calcium supplements to help restore bone mineralization. Supplements may be taken orally or given via injection.
- Dietary changes: Eating a diet rich in calcium and vitamin D can help support bone health. Calcium-rich foods include dairy products, leafy greens, and fortified cereals, while vitamin D can be obtained through sunlight exposure or supplements.
- Medications: Prescription medications may be recommended to help increase bone mineral density and reduce fracture risk.
- Monitoring: Regular blood tests to monitor vitamin D, calcium, and phosphate levels are important for people with osteomalacia.
- Underlying causes: Treating underlying conditions that may be contributing to the vitamin D, calcium, or phosphate deficiency is important, such as malabsorption syndromes or chronic kidney disease.