Gout
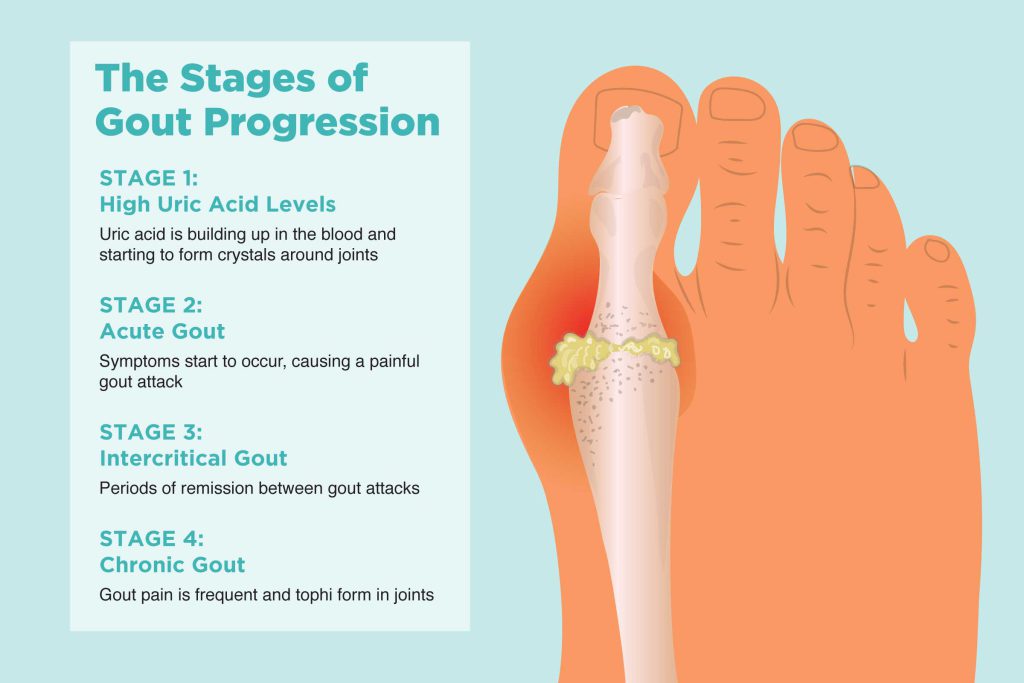
Gout is a type of arthritis that occurs when uric acid crystals accumulate in the joints, leading to inflammation and pain. Uric acid is a waste product that is normally excreted by the kidneys, but in some people, the body produces too much of it or the kidneys cannot excrete it properly.
Gout typically affects the joints of the big toe, but it can also affect other joints, such as the ankles, knees, wrists, and elbows. The symptoms of gout can include:
- Sudden and intense pain in the affected joint
- Swelling, redness, and warmth in the affected joint
- Limited range of motion in the affected joint
- Fever and chills (in severe cases)
Gout attacks can be triggered by certain foods and beverages, such as red meat, shellfish, alcohol, and sugary drinks. Other factors that can increase the risk of gout include obesity, high blood pressure, diabetes, and a family history of the condition.
Treatment for gout typically involves managing pain and inflammation with nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), such as ibuprofen, and colchicine. Medications that lower uric acid levels, such as allopurinol or febuxostat, may also be prescribed to prevent future gout attacks. Lifestyle changes, such as weight loss and dietary modifications, can also help manage gout symptoms and prevent future attacks.
It is important to seek medical attention if you are experiencing symptoms of gout, as early diagnosis and treatment can help prevent joint damage and other complications.