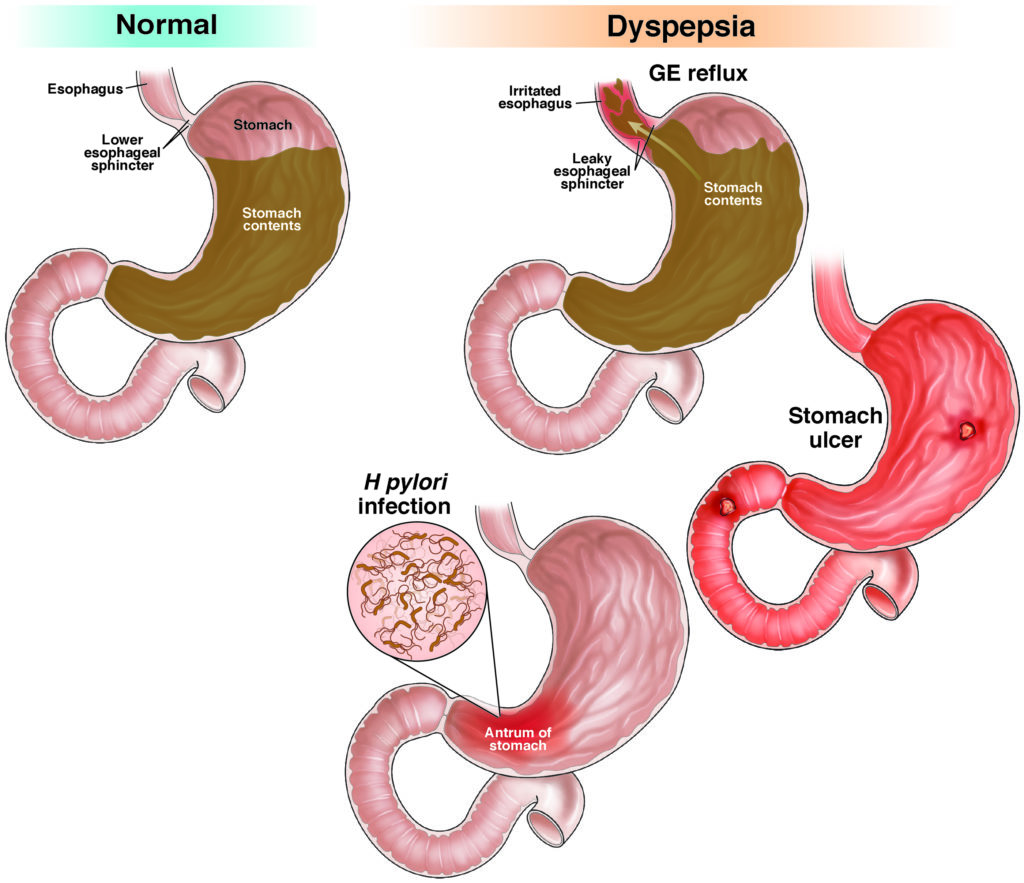
Dyspepsia
Dyspepsia is a medical condition that is characterized by discomfort or pain in the upper abdomen, often accompanied by bloating, nausea, and a feeling of fullness after eating. It can be caused by a variety of factors, including eating too much or too quickly, consuming certain foods or drinks, or gastrointestinal conditions such as gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) or peptic ulcer disease.
The symptoms of dyspepsia can be similar to those of indigestion, and may also include belching, heartburn, and a sour taste in the mouth. In some cases, dyspepsia may be accompanied by vomiting or diarrhea.
Treatment for dyspepsia depends on the underlying cause. In some cases, lifestyle changes such as eating smaller meals, avoiding trigger foods or drinks, and reducing stress may be helpful. Over-the-counter antacids and acid blockers may also be used to help relieve symptoms.
If dyspepsia persists or is accompanied by other symptoms such as weight loss, vomiting, or difficulty swallowing, it is important to seek medical attention. Your healthcare provider can help identify the underlying cause and develop an appropriate treatment plan. In some cases, prescription medications or other therapies may be necessary to manage symptoms and treat underlying conditions.