Dysentery
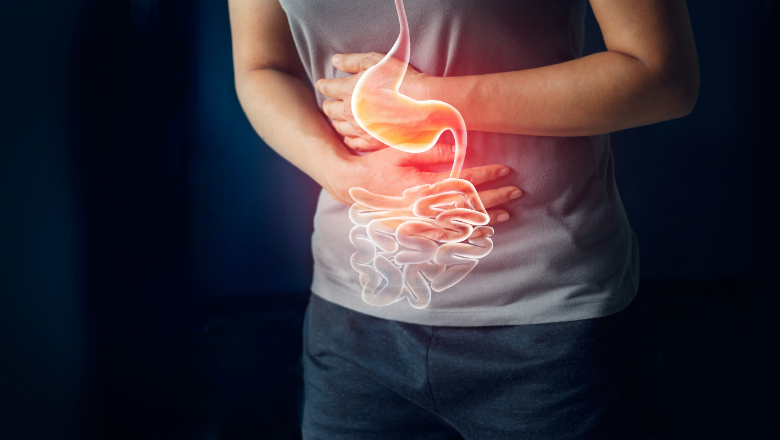
Dysentery is a medical condition that causes inflammation and irritation of the intestines, resulting in severe diarrhoea that is often bloody, and abdominal pain. The condition can be caused by a variety of bacterial, viral, and parasitic infections.
Symptoms of dysentery include frequent, watery stools that are often accompanied by blood and mucus, abdominal cramps, and fever. In severe cases, dysentery can cause dehydration, which can be life-threatening, especially in young children, the elderly, and people with weakened immune systems.
Treatment for dysentery usually involves the use of antibiotics to combat the bacterial infection. In some cases, medication may also be given to help relieve symptoms such as pain and fever. It is important to drink plenty of fluids to prevent dehydration, especially if the diarrhoea is severe or prolonged.
Preventing dysentery involves maintaining good hygiene practices such as washing hands regularly, using clean water for drinking and cooking, and avoiding contaminated food and water sources. If you are travelling to an area where dysentery is common, it is important to take appropriate precautions such as drinking bottled water and avoiding raw fruits and vegetables that may have been washed in contaminated water.