Cryptococcosis
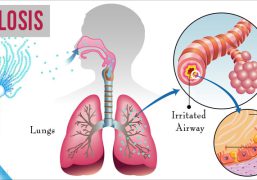
Cryptococcosis is a type of fungal infection caused by the fungus Cryptococcus neoformans. The fungus is found in soil, bird droppings, and other environmental sources. The infection typically affects individuals with weakened immune systems, such as those with HIV/AIDS, or those undergoing chemotherapy or organ transplantation.
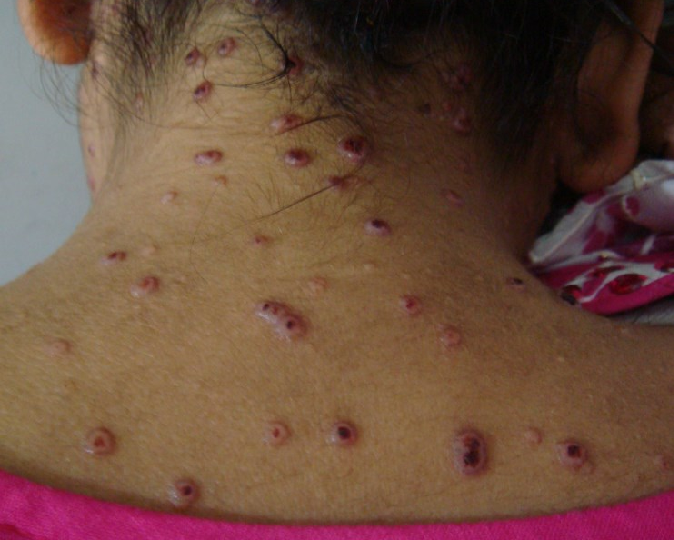
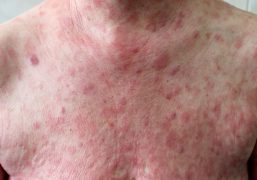
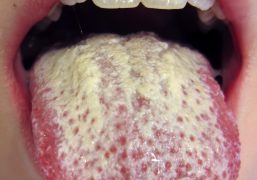
Symptoms of cryptococcosis can vary depending on the severity of the infection and the part of the body affected. Common symptoms may include headache, fever, cough, chest pain, shortness of breath, and confusion. In some cases, the infection can spread to the brain, causing meningitis or encephalitis.
Diagnosis of cryptococcosis typically involves laboratory testing of samples of blood, urine, or spinal fluid. Treatment may involve the use of antifungal medications, such as amphotericin B or fluconazole, which can be administered orally or intravenously.
Prevention of cryptococcosis involves avoiding exposure to the fungus by wearing protective clothing and practicing good hygiene in environments where the fungus may be present, such as bird roosting sites or areas with large amounts of soil or decaying plant material. Individuals with weakened immune systems should also take extra precautions to avoid exposure to the fungus.