Bronchitis
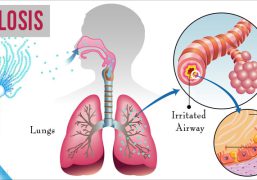
Bronchitis is an inflammation of the bronchial tubes, which are the airways that carry air to the lungs. It is most often caused by a viral or bacterial infection, but can also be caused by irritants such as tobacco smoke, air pollution, or allergens.
The symptoms of bronchitis may include coughing, chest discomfort or pain, fatigue, shortness of breath, wheezing, and low-grade fever. Acute bronchitis typically lasts for a few weeks and can be self-limiting, while chronic bronchitis is a long-term condition that can lead to other respiratory problems such as COPD.
Diagnosis of bronchitis is typically made through a physical exam and review of symptoms, and may also involve chest X-rays, pulmonary function tests, or sputum tests to rule out other conditions.
Treatment for bronchitis typically involves supportive care such as rest, hydration, and over-the-counter pain and fever relievers. Antibiotics may be prescribed in cases of bacterial bronchitis, but are not effective for viral bronchitis. Bronchodilators and corticosteroids may also be used to help relieve symptoms and improve breathing.
Prevention of bronchitis involves avoiding exposure to irritants such as tobacco smoke and air pollution, and practicing good respiratory hygiene such as washing hands frequently and covering the mouth and nose when coughing or sneezing.
It is important to seek medical attention if you experience severe or persistent symptoms of bronchitis, as it can lead to other respiratory problems if left untreated.