Hepatitis
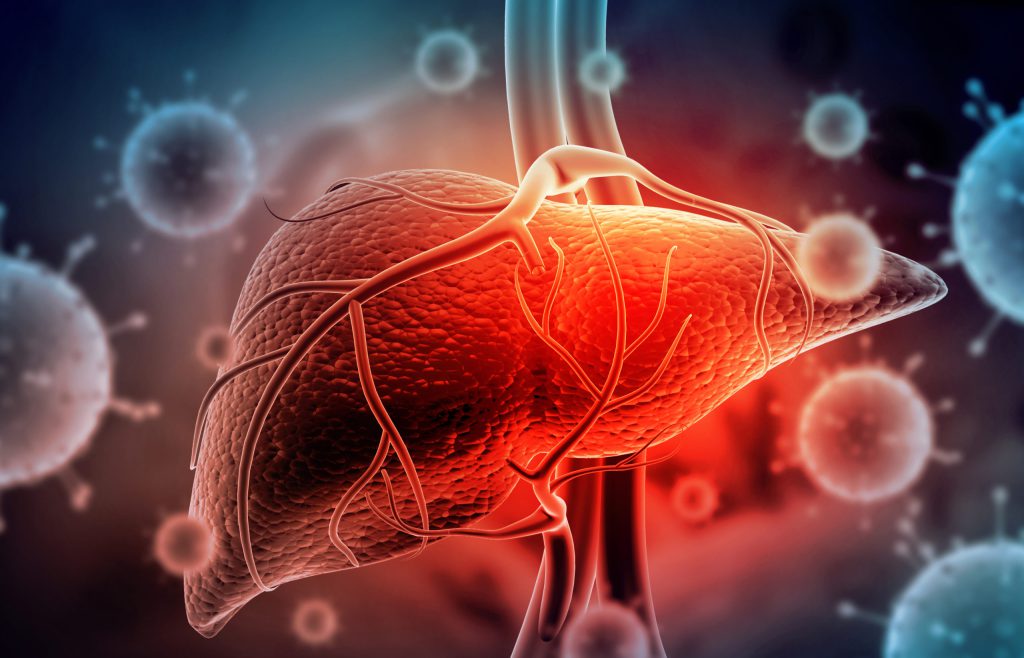
Hepatitis is a medical condition that is characterized by inflammation of the liver. There are several types of hepatitis, including hepatitis A, B, C, D, and E, each of which is caused by a different virus. The symptoms of hepatitis may include fatigue, abdominal pain, jaundice (yellowing of the skin and eyes), and flu-like symptoms such as fever and nausea.
Hepatitis A and E are usually spread through contaminated food or water, while hepatitis B, C, and D are spread through blood and bodily fluids, such as through unprotected sex or sharing of needles. Some forms of hepatitis can also be spread from mother to child during childbirth.
Treatment for hepatitis depends on the type and severity of the infection. In some cases, the infection may clear up on its own without any treatment, while in other cases, antiviral medications may be used to help fight the virus and reduce inflammation.
Prevention of hepatitis involves practicing good hygiene, such as washing hands frequently, and avoiding exposure to contaminated food, water, or bodily fluids. Vaccines are available for hepatitis A and B, and are recommended for those at high risk of infection.
It is important to seek medical attention if symptoms of hepatitis develop, as untreated hepatitis can lead to liver damage, cirrhosis, or liver failure.