COPD
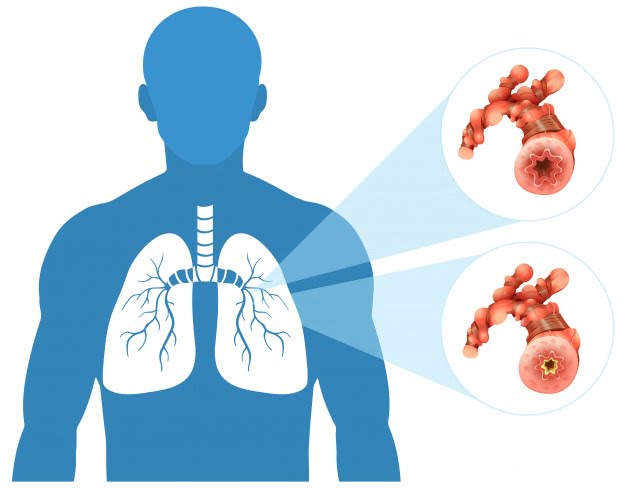
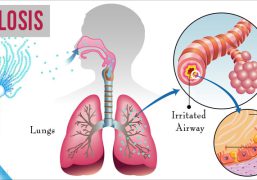
Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD) is a chronic lung disease that causes obstructed airflow in the lungs, making it difficult to breathe. The two main types of COPD are chronic bronchitis and emphysema.
The primary cause of COPD is long-term exposure to irritants that damage the lungs, such as cigarette smoke, air pollution, and occupational dust and chemicals. Genetics and respiratory infections may also contribute to the development of COPD.
The symptoms of COPD typically include shortness of breath, wheezing, chronic cough, and excess mucus production. As the disease progresses, individuals may experience fatigue, chest pain, and frequent respiratory infections.
Diagnosis of COPD is typically made through a combination of medical history, physical exam, lung function tests, and imaging tests such as chest X-rays or CT scans.
Treatment for COPD typically involves lifestyle changes such as quitting smoking, avoiding lung irritants, and engaging in regular exercise. Medications such as bronchodilators and steroids may also be prescribed to help manage symptoms and reduce inflammation in the airways.
In more severe cases of COPD, oxygen therapy and pulmonary rehabilitation may be necessary. In some cases, surgical procedures such as lung volume reduction surgery or lung transplantation may be considered.
Prevention of COPD involves avoiding exposure to lung irritants and practicing good respiratory hygiene, such as washing hands frequently and avoiding close contact with individuals who are sick.
It is important to seek medical attention if you have symptoms of COPD or if you have been diagnosed with the disease, as early intervention and management can help to slow the progression of the disease and improve quality of life.