Asthma
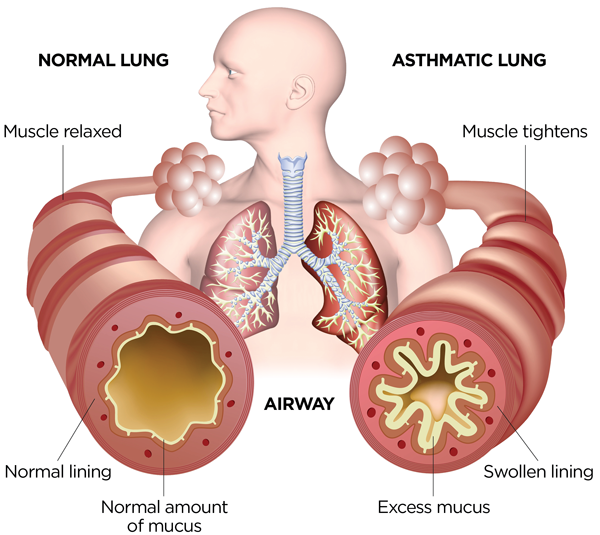
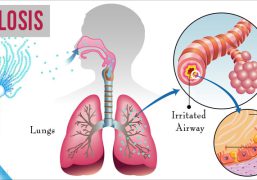
Asthma is a chronic respiratory disease characterized by inflammation and narrowing of the airways, which can make breathing difficult. Common symptoms of asthma include wheezing, coughing, chest tightness, and shortness of breath.
Asthma is caused by a combination of genetic and environmental factors, such as exposure to allergens (such as pollen, dust mites, and pet dander), respiratory infections, air pollution, and exercise.
Treatment for asthma usually involves two types of medications: quick-relief medications, such as bronchodilators, that are used to provide immediate relief of symptoms, and long-term control medications, such as inhaled corticosteroids, that are used to reduce inflammation and prevent asthma attacks.
In addition to medication, people with asthma may benefit from lifestyle changes, such as avoiding triggers that can worsen symptoms, getting regular exercise, maintaining a healthy weight, and quitting smoking (if applicable). Asthma management also involves monitoring symptoms, tracking peak flow measurements, and having a written asthma action plan in case of an emergency. With proper management, most people with asthma are able to live normal, active lives.