Ankylosing spondylitis
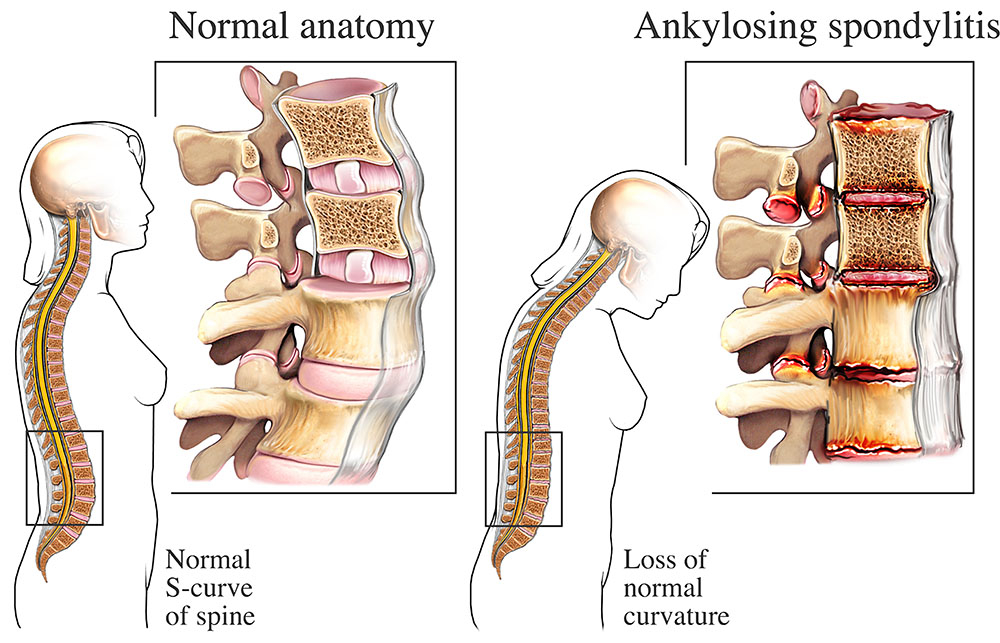
Ankylosing spondylitis (AS) is a type of inflammatory arthritis that primarily affects the spine, although other joints may also be involved. It is a chronic condition that causes inflammation in the joints and can lead to pain and stiffness in the affected areas.
The cause of ankylosing spondylitis is not completely understood, but it is believed to be an autoimmune disorder, in which the body’s immune system mistakenly attacks its own tissues, leading to inflammation. Genetic factors are also thought to play a role in the development of the condition.
Symptoms of ankylosing spondylitis typically develop gradually and include lower back pain and stiffness that may worsen at night or after periods of inactivity. Other symptoms may include pain and stiffness in the neck, hips, shoulders, and chest. In severe cases, ankylosing spondylitis can lead to fusion of the vertebrae, resulting in a fixed, rigid spine.
Treatment for ankylosing spondylitis aims to relieve pain and stiffness, prevent deformities, and maintain mobility. Treatment may include medications such as nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (DMARDs), and biologic agents, as well as physical therapy and exercise. In severe cases, surgery may be required to replace damaged joints or to correct spinal deformities.